Azure Blob Storage is a powerful service for storing large amounts of unstructured data — things like documents, logs, images, or backups. But with great data comes great responsibility — you need to protect it.
Instead of using access keys or connection strings (which are hard to manage securely), Azure recommends Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) to give fine-grained, secure access to your resources. In this post, we’ll walk through how to set that up in a Python app.
🌟 Why Use Azure RBAC for Blob Storage?
Here are some strong reasons why using RBAC is a good move:
- ✅ No more hardcoded keys – You can stop worrying about rotating or accidentally leaking access keys.
- ✅ Fine-grained control – Assign specific roles like Reader or Blob Data Reader to apps or users.
- ✅ Follows least privilege principle – Only the minimum required access is granted.
🔄 Overall Workflow:
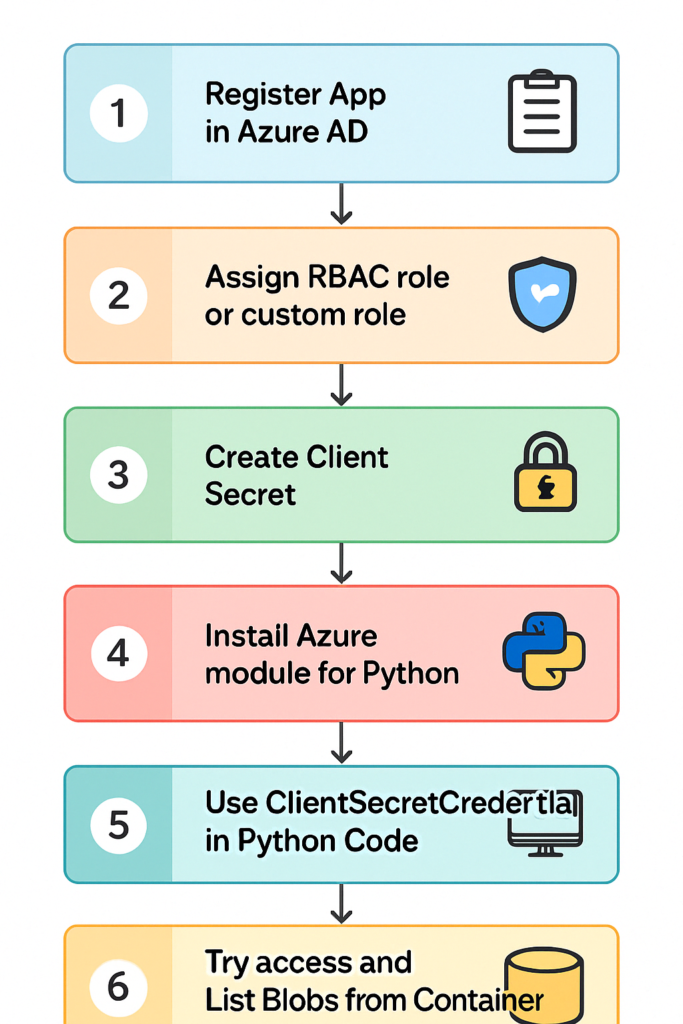
🧑💻 Step-by-Step Guide:
Step 1: Register Your App in Azure AD
Go to Azure Portal → Microsoft Entra ID (formerly Azure AD)
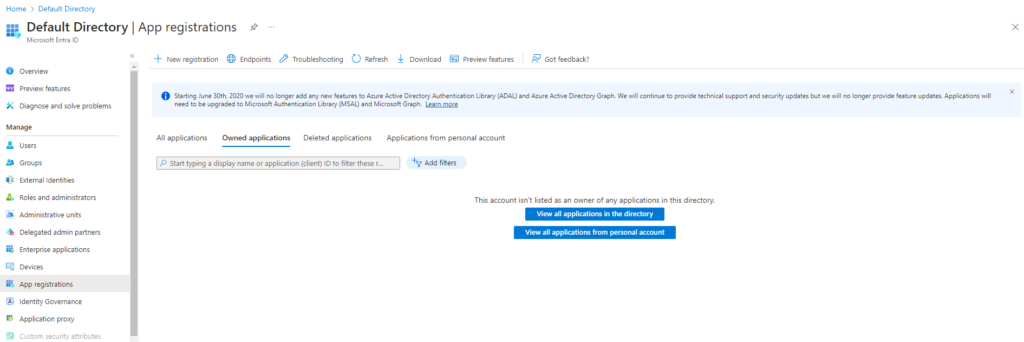
Select App registrations → New registration
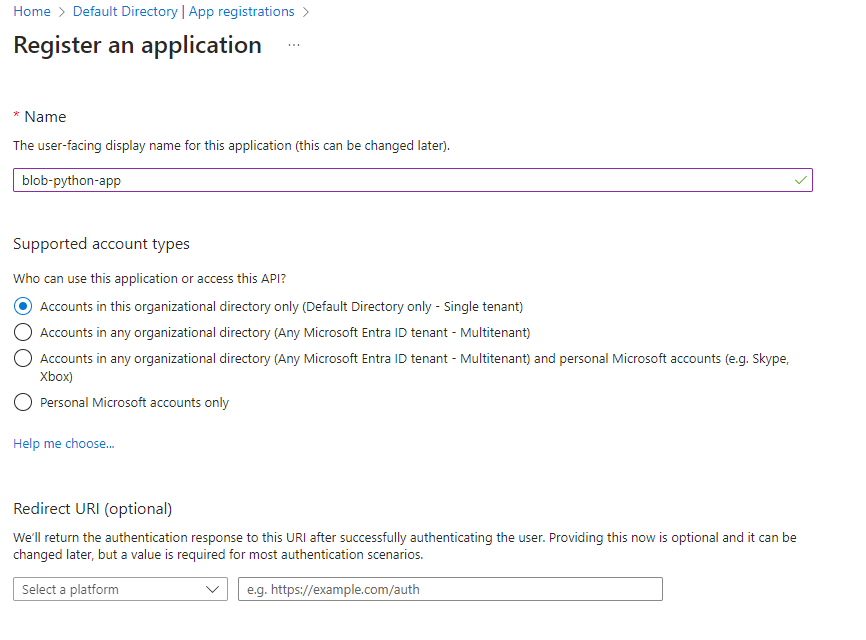
Name your app and finish the registration
Save your Application (client) ID and Directory (tenant) ID for later
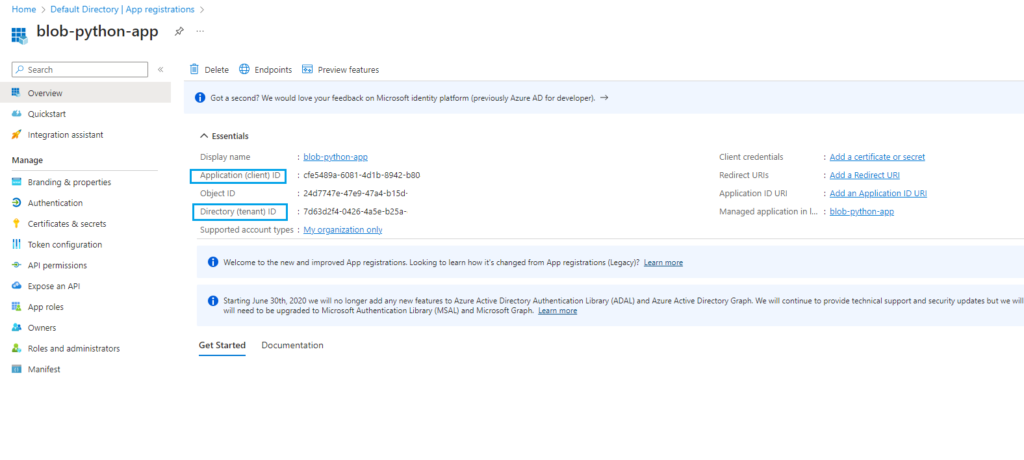
Step 2: Assign RBAC Roles to the App
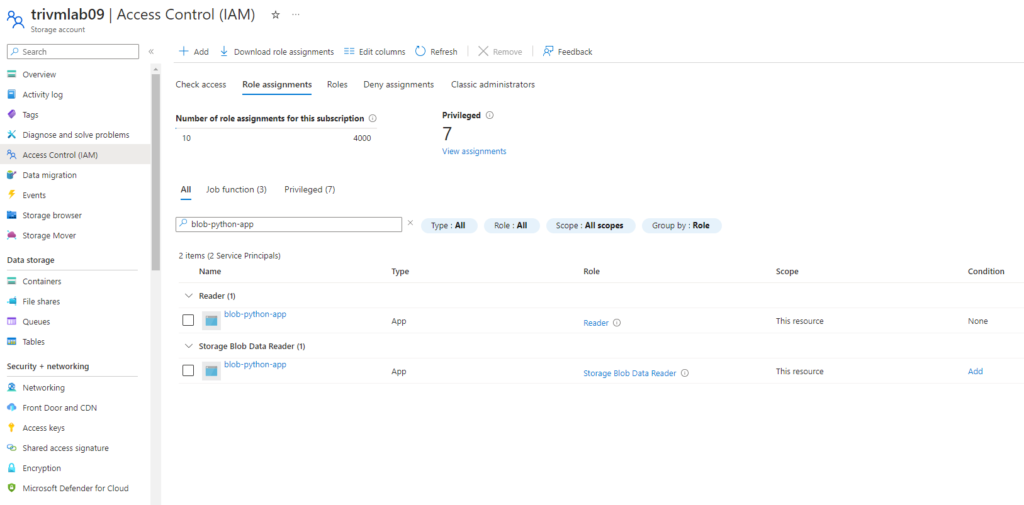
– Need configure RBAC with 2 role assignment include: Read Only and Storage Blob Data Reader for application on Storage Account level.
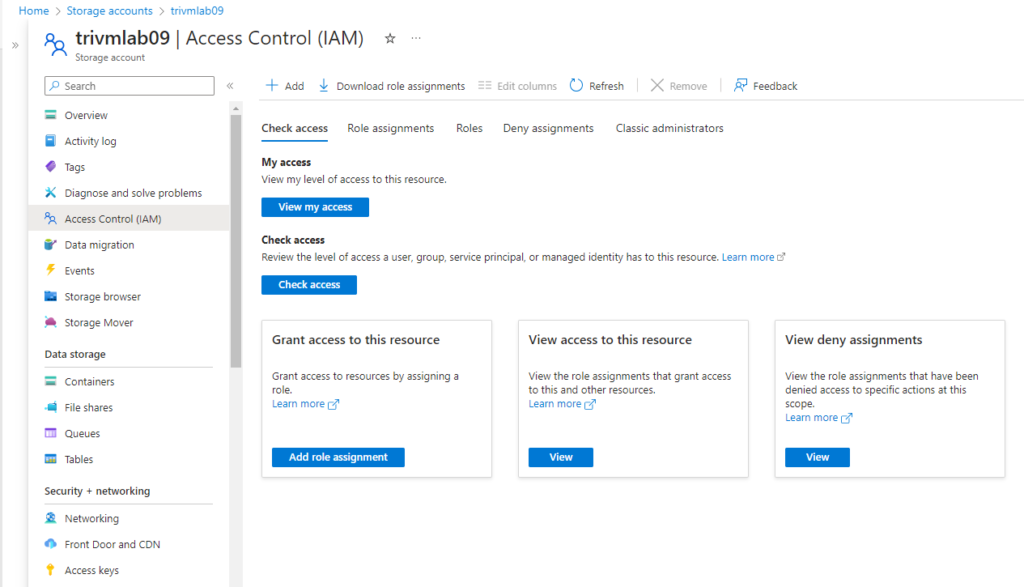
- Navigate to your Storage Account
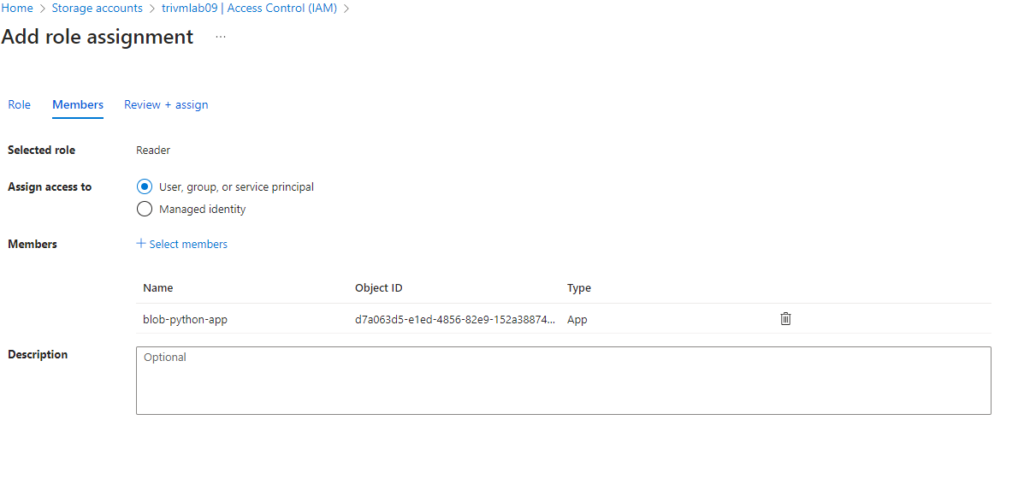
- Go to Access Control (IAM) → Add role assignment
- Assign:
- Reader role (for general access to storage account)
- Storage Blob Data Reader (for blob-specific access)
4. Choose the App registration as the principal
5. Add role assignment same for role Storage Blob Data Reader
Step 3: Create a Client Secret
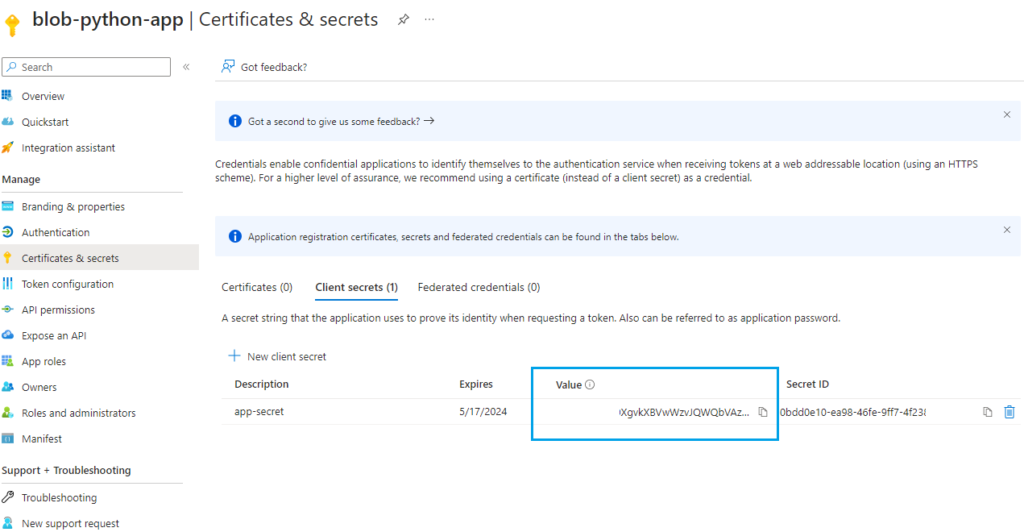
- In App registrations, find your app > Go to Certificates & secrets → New client secret
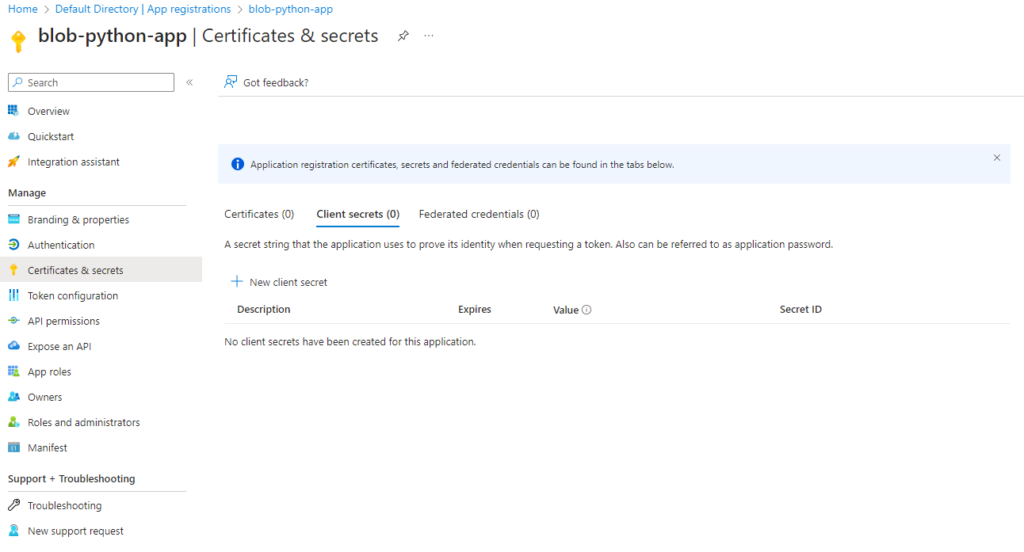
2. Add a description and set an expiration period
3. Copy and securely store the Value ( input to your app code)
Step 4: Install Azure Module for Python
# pip install azure-storage-blob azure-identity
# pip install azure-storage-blob[aio]
Step 5: Authenticate and Access Blobs with Python
Here’s a full working code to authenticate and list content in container of Azure Blob Storage:
# This script using Azure AD application RBAC for gant access to Azure Blob Storage
# Need create application registration in Azure AD configure RBAC access to Storage Account fisrt
# Version 1- Tto1991
from azure.identity import DefaultAzureCredential
from azure.storage.blob import BlobServiceClient, BlobClient, ContainerClient
from azure.identity import ClientSecretCredential
tenant_id = "xxx"
app_id= "xxx"
app_access_key = "xxx"
storage_uri = "xxx"
container_name = "ebooks"
azure_credential = ClientSecretCredential(
tenant_id = tenant_id,
client_id = app_id,
client_secret = app_access_key,
)
blob_service_client = BlobServiceClient(account_url=storage_uri,credential=azure_credential)
container_name = "new-ebooks"
#Create a blob client using the local file name as the name for the blob
container_client = blob_service_client.get_container_client("ebooks")
blob_list = container_client.list_blobs()
for blob in blob_list:
print(f"File in container: {container_name}" + blob.name)✅ Summary:
By using Azure RBAC and ClientSecretCredential in your Python application, you:
- Get secure access to Blob Storage without keys
- Follow Azure best practices
- Set up a foundation that scales with enterprise-grade security
This approach is great for production environments where you care about access management, compliance, and minimizing secrets.
“Security isn’t just a configuration—it’s a mindset. Build with clarity, access with intention.”
— TechNoStress